The menstrual cycle is essential to women’s reproductive health, influencing fertility and overall well-being. Despite its importance, many women may not fully understand the intricate processes within their bodies each month. Gaining a thorough understanding of the four phases of the menstrual cycle—menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal—can empower women to better manage their health.
This knowledge is critical for recognizing what’s normal and identifying potential concerns that may require medical attention. With advancements in gynecology and accessible healthcare, women have more tools than ever to monitor and support their reproductive health effectively.
What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a natural, recurring series of hormonal and physiological changes that prepare a woman’s body for potential pregnancy. It begins at puberty and continues until menopause, encompassing a predictable pattern that varies slightly from one woman to another.
Each phase of the cycle is driven by specific hormonal fluctuations that regulate ovulation and the preparation or shedding of the uterine lining. Irregularities in the cycle may signal underlying conditions that require professional evaluation, such as hormonal imbalances or reproductive disorders. Regular visits to a gynecologist and routine health checks, such as a pap smear test, are essential for maintaining reproductive health.
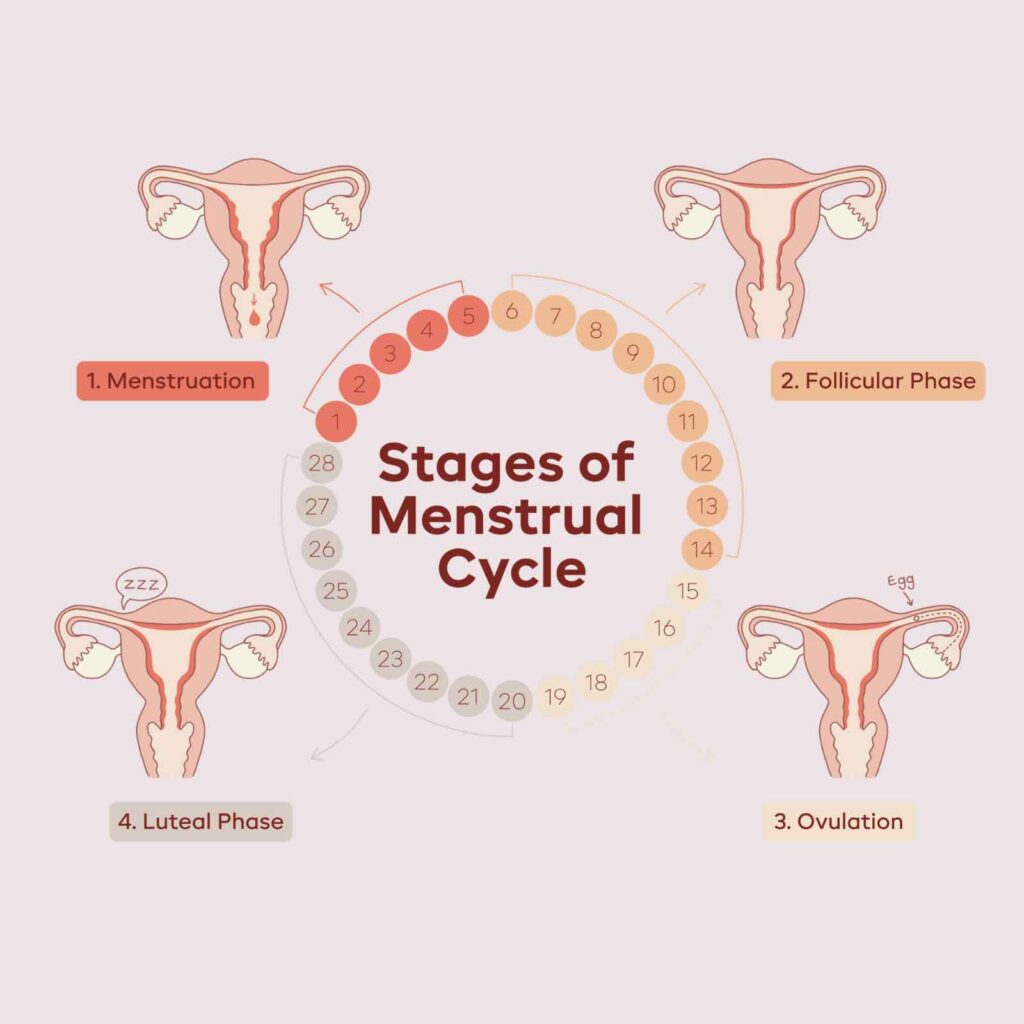
Overview of the Four Phases
- Menstrual Phase: This is the first phase of the cycle, marked by the shedding of the uterine lining when pregnancy does not occur. It’s characterized by bleeding, typically lasting 3–7 days.
- Follicular Phase: Beginning simultaneously with the menstrual phase, this stage involves the stimulation of ovarian follicles by hormones like Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH). Estrogen levels begin to rise, preparing the uterine lining for potential implantation.
- Ovulation: At the midpoint of the cycle, ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from the ovary. This phase is crucial for conception and is triggered by a Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surge.
- Luteal Phase: The final phase of the cycle involves preparing the uterine lining for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, hormone levels drop, signaling the start of a new cycle.
Each phase plays a vital role in reproductive health, and disruptions in these processes may require evaluation by a healthcare provider.
The Importance of Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
Awareness of the menstrual cycle phases goes beyond fertility—it helps women maintain their overall health. By tracking symptoms and patterns, women can identify irregularities such as heavy bleeding, missed periods, or extreme pain. These signs could indicate underlying conditions like endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or hormonal imbalances that might require intervention from an endometriosis specialist or a gynecologist.
In addition to tracking the cycle, regular healthcare practices, such as scheduling pap smear tests and routine ultrasounds, are essential. These procedures can detect early signs of cervical abnormalities, uterine conditions, or other reproductive health concerns.
The Menstrual Phase: Shedding and Renewal
The menstrual phase is the first stage of the menstrual cycle and is often called the period. It marks the shedding of the uterine lining, which occurs when pregnancy does not occur.
This phase is a natural process of renewal, clearing the body to begin the next cycle. Understanding the menstrual phase is key to recognizing what is normal and identifying when medical attention may be necessary. Women experiencing discomfort or irregularities during this phase can benefit from regular obgyn care to ensure optimal reproductive health.
What Happens During the Menstrual Phase?
The menstrual phase begins with a significant drop in estrogen and progesterone hormones, signaling the body to shed the thickened uterine lining. This process involves the discharge of blood and tissue through the cervix and vagina. Women may experience a range of physical symptoms, including cramps, fatigue, and mood swings, caused by hormonal fluctuations and uterine contractions.
While these symptoms are common, severe discomfort or irregularities may point to underlying conditions such as endometriosis or hormonal imbalances. In such cases, consulting an endometriosis specialist or a gynecologist is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.
How Long Does the Menstrual Phase Last?
The menstrual phase typically lasts 3 to 7 days, but the duration can vary significantly from one woman to another. Factors like age, hormonal levels, and overall health can influence the length and flow of the period.
Irregularities such as hefty bleeding, prolonged periods, or skipped cycles may warrant further investigation. For example, conditions like endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to abnormal menstrual patterns. Seeking routine obgyn care helps address these concerns early, offering tailored treatments to restore balance and improve quality of life.
The Follicular Phase: Preparing for Ovulation
The follicular phase is the second stage of the menstrual cycle and begins right after the menstrual phase. This phase is essential for preparing the body for ovulation, involving key hormonal changes and physiological adjustments.
Understanding the follicular phase highlights the body’s intricate preparation for potential pregnancy and provides insight into how women can optimize their health and lifestyle during this time. Routine gynecology care can help monitor any irregularities that may occur in this phase.
Key Hormonal Changes in the Follicular Phase
The pituitary gland initiates the follicular phase by releasing Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH). This hormone stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, each containing an immature egg. As the follicles develop, they produce estrogen, which is critical in preparing the uterine lining (endometrium) for a possible pregnancy.
The rising estrogen levels also signal the body to slow the release of FSH, ensuring that only the most viable follicle reaches maturity. This intricate hormonal dance underscores the importance of regular checkups with an obgyn specialist to ensure that the reproductive system functions effectively.
Physical and Emotional Changes During the Follicular Phase
The increase in estrogen during the follicular phase positively impacts both physical and emotional well-being. Women often report improved energy levels, enhanced mood, and greater mental clarity. This is also a time when skin health tends to improve due to the hormone’s ability to stimulate collagen production and reduce inflammation.
Physically, women may notice heightened stamina and endurance, making this phase ideal for engaging in physical activities or tackling demanding tasks. Understanding these changes can help women align their lifestyle and productivity with their cycle. Regular consultations with a gynecologist can provide personalized advice on how to maximize well-being during this phase.
Ovulation Phase: The Release of the Egg
The ovulation phase is a pivotal moment in the menstrual cycle, marking the release of a mature egg ready for fertilization. This phase typically occurs mid-cycle and is essential for conception.
Understanding the ovulation phase benefits women planning for pregnancy and provides insight into reproductive health. Women who experience irregularities or challenges in this phase can greatly benefit from regular consultations with an endometriosis specialist or obgyn care to address any underlying concerns.
What Triggers Ovulation?
Ovulation is initiated by a surge in Luteinizing Hormone (LH), a key hormone released by the pituitary gland. This surge prompts the dominant follicle in the ovary to release its mature egg. Once released, the egg travels through the fallopian tube, which remains viable for approximately 24 hours, awaiting fertilization.
The timing of ovulation is critical for conception, making this phase a central focus for women actively trying to conceive. Accurate tracking of ovulation can be enhanced through regular monitoring with an obstetrician or gynecologist, ensuring optimal timing for family planning.
Recognizing Signs of Ovulation
Identifying ovulation signs is valuable for understanding fertility windows. Some common indicators include:
- Changes in cervical mucus consistency: Mucus becomes clear, stretchy, and similar in texture to raw egg whites, facilitating sperm mobility.
- A slight rise in basal body temperature: A small but noticeable temperature increase occurs after ovulation due to rising progesterone levels.
- Ovulatory pain: Mittelschmerz is a mild cramping sensation felt on one side of the abdomen.
These physical changes are natural cues that can be tracked for family planning purposes. For women who may struggle with conception or have irregular cycles, discussions with an obgyn specialist during obstetrics appointments can offer tailored advice and solutions.
The Luteal Phase: Preparing for Implantation or Resetting the Cycle
The luteal phase is the final stage of the menstrual cycle, occurring after ovulation and before menstruation begins. This phase is crucial for determining whether the body will prepare for pregnancy or reset for the next cycle.
The hormonal changes in this phase significantly impact both physical and emotional well-being, making it essential for women to understand their bodies during this time. For those experiencing irregularities or severe symptoms, consulting an obgyn specialist can provide valuable insights and relief.
Hormonal Shifts in the Luteal Phase
Following ovulation, progesterone becomes the dominant hormone during the luteal phase. This increase thickens the uterine lining to support the potential implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, progesterone and estrogen levels drop, signaling the body to shed the uterine lining and begin the next menstrual cycle.
These hormonal fluctuations regulate the cycle and influence various physical and emotional states. Women experiencing disruptions in this phase, such as irregular cycles or hormonal imbalances, may benefit from gynecology care or hormonal therapy to restore balance and alleviate discomfort.
PMS and Other Symptoms of the Luteal Phase
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) is commonly associated with the luteal phase, manifesting as both physical and emotional symptoms. Common indicators include:
- Mood swings and irritability: Often driven by hormonal changes, these symptoms can affect daily interactions and emotional well-being.
- Bloating and breast tenderness: Progesterone can lead to water retention and sensitivity, contributing to discomfort
- Fatigue and food cravings: The body’s metabolic shifts during this phase may cause low energy and cravings for carbohydrates or sweets.
While these symptoms are typical, persistent or severe discomfort may signal underlying issues. Women experiencing debilitating premenstrual symptoms should consider consulting their gynecologist or exploring menopause treatments and hormonal therapies as part of their long-term care strategy.
Understanding and Supporting Your Menstrual Health
Maintaining awareness of the menstrual cycle is more than tracking dates—it’s a step toward proactive health management. Each phase of the cycle offers insights into your overall well-being, allowing you to address changes and seek professional care when necessary. At Gwinnett OB/GYN, we provide the resources and expertise to help women navigate and optimize their menstrual health.
How Gwinnett OB/GYN Can Support Your Health
Gwinnett OB/GYN offers a wide range of services designed to address menstrual health at every stage of life. Our expert team provides:
- Routine pap smear tests to screen for cervical health and detect abnormalities early.
- Advanced diagnostic ultrasound services, including 3D and 4D imaging, to identify and monitor reproductive conditions.
- Support from skilled gynecologists and endometriosis specialists, offering tailored care for menstrual irregularities or conditions like endometriosis.
- Comprehensive menopause treatments for women navigating hormonal transitions later in life.
Combined with our compassionate approach, these services ensure every patient receives personalized, expert care.
Take Action Today
Your reproductive health is a priority. Whether you’re managing irregular cycles, planning for pregnancy, or addressing symptoms of conditions like endometriosis, our team at Gwinnett OB/GYN is here to support you.
Schedule an appointment with Gwinnett OB/GYN today to take the first step toward comprehensive and personalized care. With our experienced providers, advanced diagnostics, and patient-first approach, we are committed to helping you achieve optimal health and well-being.